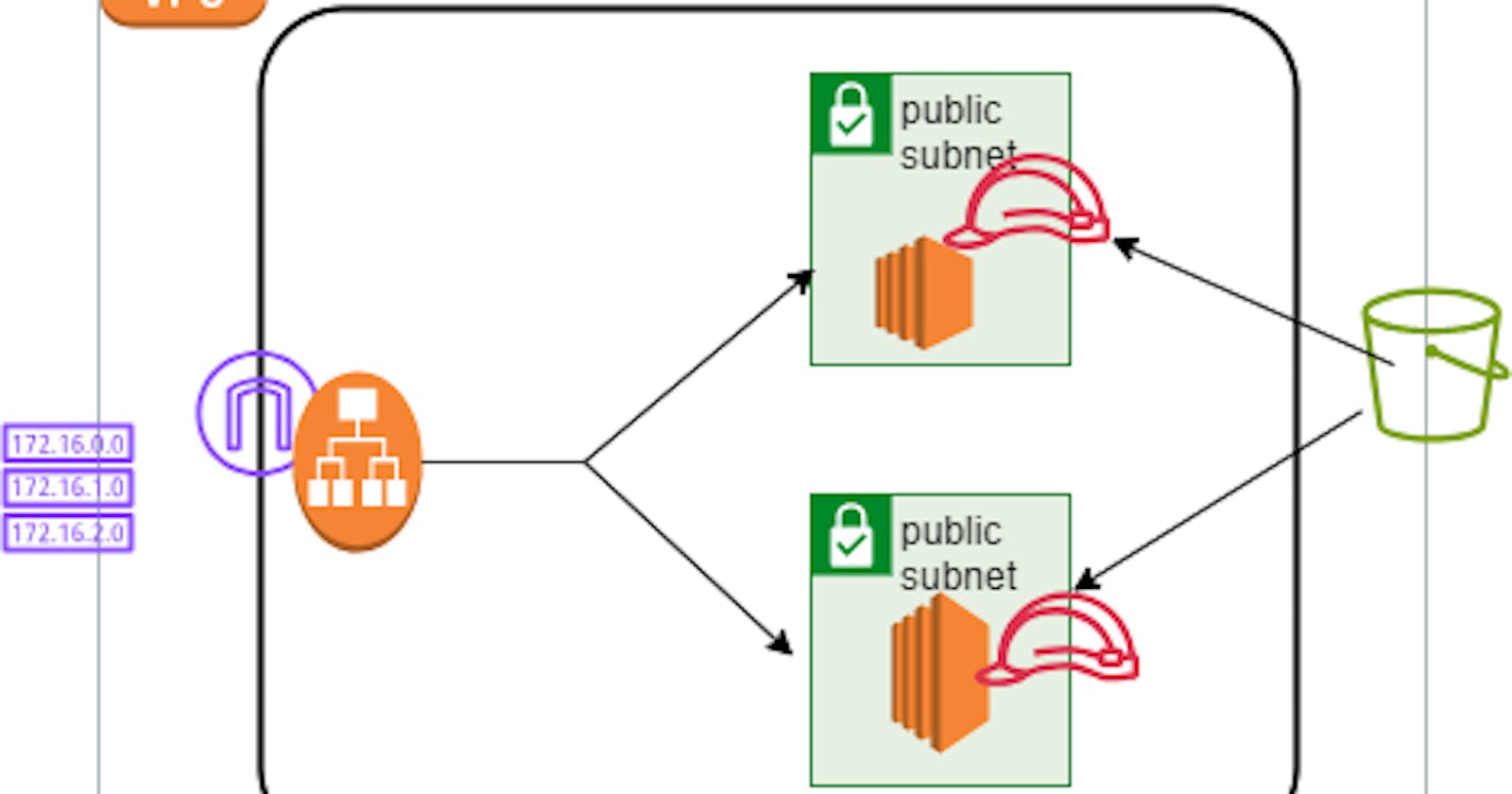
This Terraform configuration sets up a basic infrastructure with a VPC, subnets, security groups, S3 bucket, EC2 instances, an ALB, and IAM roles.
Github repo: https://github.com/Pardeep32/terraform-projects-serious.git
Step 1: Create an AWS Account
Go to the AWS website: aws.amazon.com.
Follow the instructions to create an AWS account.
Here's a breakdown of the resources and their purposes:
Step 2: Create an IAM User
Log in to the AWS Management Console using your AWS account credentials.
In the "Services" menu, select "IAM" under "Security, Identity, & Compliance".

In the IAM dashboard, click on "Users" in the left navigation pane.
Click on the "Add user" button.

Enter a username for the IAM user (e.g., "terraform-user").

Select "Programmatic access" as the access type.
Click on "Next: Permissions".

Choose "Attach existing policies directly".
Search for and select the "AmazonS3FullAccess" policy.
Click on "Next: Tags" (optional).
Click on "Next: Review".
Review the user settings and click on "Create user".
Save the "Access key ID" and "Secret access key" provided. These will be used as the AWS credentials in your Terraform configuration.

Step 3: Install and Configure Terraform
Download and install Terraform from the official website: terraform.io.
Create a new directory for your Terraform project.
Create a new file named
main.tfin the project directory.Add the following code to
provider.tf
The AWS provider in Terraform enables users to manage AWS resources using code, providing a declarative approach to infrastructure management. It offers features such as dependency management, state management, plan and apply commands, execution plans, remote state storage, and support for multiple cloud providers. This allows for automation, repeatability, and scalability in managing AWS infrastructure.terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "5.38.0" } } } provider "aws" { # Configuration options region = var.region }Add the following code to
variable.tf:variable "region" { default = "ca-central-1" } variable "cidr" { default = "10.0.0.0/16" }Add the following code to
main.tf: each block is explained as below-
VPC (
aws_``vpc.myvpc):Creates a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with the CIDR block specified in the variable
var.cidr.resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" { cidr_block = var.cidr tags = { Name = "myvpc" } }
Subnets (aws_subnet.subnet1 and aws_subnet.subnet2):
Creates two subnets in the VPC, each in a different availability zone (
${var.region}aand${var.region}b).resource "aws_subnet" "subnet1" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id availability_zone = "${var.region}a" cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/24" map_public_ip_on_launch = true } resource "aws_subnet" "subnet2" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id availability_zone = "${var.region}b" cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24" map_public_ip_on_launch = true }
Internet Gateway (aws_internet_gateway.gw):
Creates an Internet Gateway and attaches it to the VPC to allow internet access.
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "gw" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id tags = { Name = "internet-gateway" } }
Route Table (aws_route_table.Route-table):
Creates a route table for the VPC with a default route to the Internet Gateway.
resource "aws_route_table" "Route-table" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id # since this is exactly the route AWS will create, the route will be adopted route { cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.gw.id } }
Route Table Association (aws_route_table_association.Rtable1 and aws_route_table_association.Rtable2):
Associates the route table with the subnets.
resource "aws_route_table_association" "Rtable1" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet1.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.Route-table.id } resource "aws_route_table_association" "Rtable2" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet2.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.Route-table.id }
Security Group (
aws_security_group.websg):Creates a security group that allows inbound traffic on ports 22 (SSH), 80 (HTTP), and 443 (HTTPS) from any IP address (
0.0.0.0/0).resource "aws_security_group" "websg" { name = "web" description = "Allow TLS inbound traffic and all outbound traffic" vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id tags = { Name = "Websg" } ingress { description = "TLS from VPC" from_port = 443 to_port = 443 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } ingress { description = "SSh from VPC" from_port = 22 to_port = 22 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } ingress { description = "http from VPC" from_port = 80 to_port = 80 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } egress { from_port = 0 to_port = 0 protocol = "-1" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } }
S3 Bucket (
aws_s3_bucket.example):Creates an S3 bucket with the specified name and tags.
# s3 bucket craetion resource "aws_s3_bucket" "example" { bucket = "deeep-tf-20244-bucket" tags = { Name = "My bucket" Environment = "Dev" } }
S3 Bucket Ownership Controls (aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls.example):
Sets the bucket ownership controls to
BucketOwnerPreferred.resource "aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls" "example" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.example.id rule { object_ownership = "BucketOwnerPreferred" } }
S3 Bucket Public Access Block (aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.example):
Configures the bucket to block public access.
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "example" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.example.id block_public_acls = false block_public_policy = false ignore_public_acls = false restrict_public_buckets = false }
S3 Bucket ACL (aws_s3_bucket_acl.example):
Sets the bucket ACL to
public-read.resource "aws_s3_bucket_acl" "example" { depends_on = [ aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls.example, aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.example, ] bucket = aws_s3_bucket.example.id acl = "public-read" }
S3 Bucket Versioning (aws_s3_bucket_versioning.versioning_example):
Enables versioning for the bucket.
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "versioning_example" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.example.id versioning_configuration { status = "Enabled" } }
EC2 Instances (
aws_instance.webserver1andaws_instance.webserver2):Creates two EC2 instances with the specified AMI, instance type, and user data script.
The instances are associated with the security group created earlier.
### instance creation resource "aws_instance" "webserver1" { ami = "ami-0a2e7efb4257c0907" # Ubuntu Server 16.04 instance_type = "t2.micro" vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.websg.id] subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet1.id user_data = base64encode(file("userdata.sh")) iam_instance_profile = aws_iam_instance_profile.example_instance_profile.name tags = { Name = "WebServer1" } } resource "aws_instance" "webserver2" { ami = "ami-0a2e7efb4257c0907" # Ubuntu Server 16.04 instance_type = "t2.micro" vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.websg.id] subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet2.id user_data = base64encode(file("userdata1.sh")) iam_instance_profile = aws_iam_instance_profile.example_instance_profile.name tags = { Name = "WebServer2" } }
Application Load Balancer (ALB) (
aws_lb.mylb):Creates an ALB with the specified name, type, security groups, and subnets.
# create application load balancer resource "aws_lb" "mylb" { name = "mylb-tf" internal = false load_balancer_type = "application" security_groups = [aws_security_group.websg.id] subnets = [aws_subnet.subnet1.id, aws_subnet.subnet2.id] tags = { Environment = "production" } }
ALB Target Group (aws_lb_target_group.mytg):
Creates a target group for the ALB with a health check on the root path (
/).resource "aws_lb_target_group" "mytg" { name = "tf-example-lb-tg" port = 80 protocol = "HTTP" vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id health_check { path = "/" interval = 5 timeout = 4 port = "traffic-port" } }
ALB Target Group Attachments (aws_lb_target_group_attachment.attach1 and aws_lb_target_group_attachment.attach2):
Attaches the EC2 instances to the target group.
# Create a new load balancer attachment resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "attach1" { target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.mytg.arn target_id = aws_instance.webserver1.id port = 80 } resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "attach2" { target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.mytg.arn target_id = aws_instance.webserver2.id port = 80 }
ALB Listener (aws_lb_listener.front_end_listener):
Creates an ALB listener on port 80 with a default action to forward traffic to the target group.
resource "aws_lb_listener" "front_end_listener" { load_balancer_arn = aws_lb.mylb.arn port = "80" protocol = "HTTP" // ssl_policy = "ELBSecurityPolicy-2016-08" // certificate_arn = "arn:aws:iam::187416307283:server-certificate/test_cert_rab3wuqwgja25ct3n4jdj2tzu4" default_action { type = "forward" target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.mytg.arn } }
IAM Role (
aws_iam_role.example_role):Creates an IAM role with a trust policy that allows EC2 instances to assume the role.
resource "aws_iam_role" "example_role" { name = "example-role" assume_role_policy = jsonencode({ "Version" : "2012-10-17", "Statement" : [ { "Effect" : "Allow", "Principal" : { "Service" : "ec2.amazonaws.com" }, "Action" : "sts:AssumeRole" } ] }) }
IAM Policy (aws_iam_policy.example_policy):
Creates an IAM policy that allows all S3 actions on all resources.
resource "aws_iam_policy" "example_policy" { name = "example-policy" description = "An example IAM policy" policy = jsonencode({ "Version" : "2012-10-17", "Statement" : [ { "Effect" : "Allow", "Action" : "s3:*", "Resource" : "*" } ] }) }
IAM Instance Profile (aws_iam_instance_profile.example_instance_profile):
Creates an IAM instance profile and associates it with the IAM role.
resource "aws_iam_instance_profile" "example_instance_profile" { name = "example-instance-profile" role = aws_iam_role.example_role.name }
Step 4: Initialize and Apply Terraform Configuration
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to your Terraform project directory.
Run
terraform initto initialize the project.
Run
terraform planto preview the changes.











Run
terraform applyto create the S3 bucket and associated resources.
Review the changes and type
yesto apply the changes.


Step 5: Verify the AWS Resources are created:
Go to the AWS Management Console.
Navigate to the EC2: 2 ec2 instances, 2 security groups, 1 load balancer and 1 target group is created.




Naviagte to IAM: 1 Iam role
example.roleis created. that is associate with 2 ec2 instances that are placed in different subnets of different availability zones ca-central-1a, ca-central-1b resp.Verify that the S3 bucket
deeep-tf-20244-buckethas been created with the appropriate permissions and versioning enabled.



- VPC is created, with 2 subnets and Route table associated with subnets, 1 internetgateway is created.




Step 6: Clean Up (Optional)
If you no longer need the resources, you can run
terraform destroyto delete the resources created by Terraform.



Notes:
Replace
YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_IDandYOUR_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYwith the access key ID and secret access key of the IAM user you created.Make sure to replace
ca-central-1with your desired AWS region in theproviderblock.This example creates an S3 bucket with versioning enabled and public read access. Customize the configuration as needed for your specific use case.
Always be cautious when storing AWS credentials. Never commit them to public repositories or share them with unauthorized individuals.
I hope this article on Terraform and AWS has been helpful in understanding how to manage AWS resources using code. If you have any further questions or need assistance, please feel free to reach out to me at Pardeep17.kp@gmail.com. I'm here to help!